The most readily accessible method for the determination of the resistance of rubber to abrasion is to use an abrasive wear tester, where a rubber piece is mounted under a weight and exposed to a rotating drum with an abrasive sheet for a fixed distance.
Related Standards
ISO 4649:2017, ASTM D5963-4 (2019)
Introduction
By far the largest use for rubber is the tire-industry where the unique properties of rubber enable robust yet flexible and gas-impermeable tires. The gradual wear of the tires against asphalt roads is an important factor both for durability but also for environmental reasons. The particulates produced are a pollution hazard and should be reduced as much as possible. The study of abrasive wear properties in a material is surprisingly complicated though. Many types of tests have been proposed and tested, such as actually running trailers in caravan with fixed weights and distances. This method of testing is limited to relative comparisons, however, and are prohibitively expensive.

Figure 1. Bareiss Abrasive Wear Tester.
In the end, the most readily accessible method is to use an abrasive wear tester where a rubber piece is mounted under a weight and exposed to a rotating drum with an abrasive sheet for a fixed distance. An example of such a machine can be seen in fig. 1. The weight difference before and after the test is registered and compared to a reference rubber with known abrasion resistance properties.
Performance
To perform an abrasive wear test is quite simple. The first step is to check the abrasive power of the abrasive sheet using a reference rubber sample. This reference rubber is available commercially. A piece of reference rubber is pre-weighed and then mounted in the machine and a full 40 m test is performed. After the test is finished, the reference rubber is weighed again. The acceptable mass loss of the rubber is between 180 and 220 mg. If the mass loss is too high, which is often the case with new abrasive sheets, a steel piece can be mounted in the sample holder to soften the abrasive sheet. A new run with reference rubber is then performed again to confirm the roughness. The test is highly reliant on the reference rubber and it needs to be used at the very least before each test and preferably after as well. In some cases it might be needed in between individual sample pieces as well.
To prepare a sample piece, use a rotating knife with a 16 mm diameter to cut buttons from a rubber sheet with a thickness of at least 6 mm. If a thinner sheet is used, it is possible to bond it to a substrate rubber for a suitable total thickness. This sample can then readily be mounted by rotating the ring outside the sample. Different downward force can be used by mounting weights on top of the sample holder. A common choice is 10 N (roughly 1 kg weights), which is also used for the reference rubber.
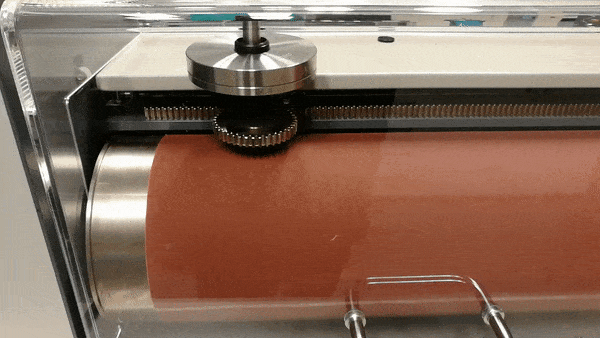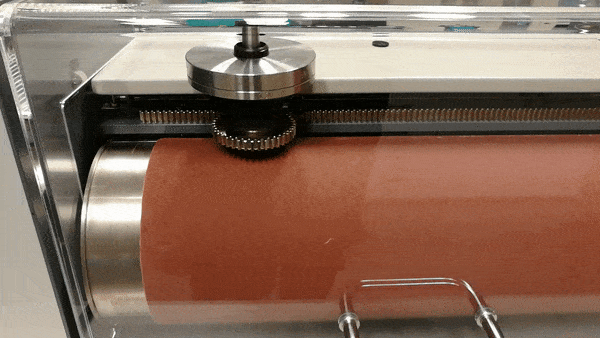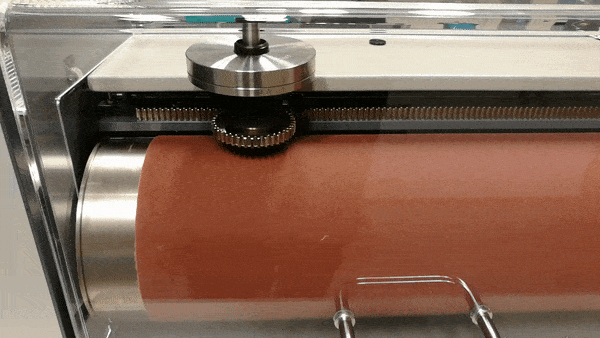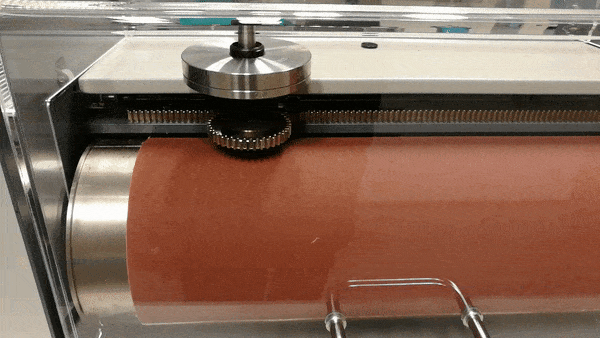
Figure 2. Showing a test in action. The sample holder is slowly moving along the axis.
Once the sample and weights are in place, the sample holder is flipped down onto the abrasive sheet and the tester rotates the drum while slowly moving the sample along the axis for a total of 20 or 40 meters on the abrasive sheet. The test in action can be seen in fig. 2. A test requires at least three samples which are weighed before and after testing. The final result is presented as an average of the lost volume of the three samples expressed as mass loss over density (Δmt/ρt), relative to the difference between a standardized mass loss of the reference rubber (Δmconst) and the actual mass loss of the reference rubber (Δmr). The final result is presented in cubic millimeters. This calculation can be seen in the formula below.

The measurement can also be performed using a rotating sample or at elevated temperatures.
Conclusion
The development of reliable testing of the very important property abrasive wear resistance has been long. The modern measurement is a best approximation test that doesn’t always produce values that correspond to real world use; however nothing better has been invented. Therefore, the ease of use and reproducible values from a rotating drum of abrasive sheets acting on a rubber sample is the most common measurement available.
Elastocon is the official Nordic representative of Bareiss and sell their equipment for abrasive wear resistance testing. We are also proud to offer testing services with a recently acquired abrasive wear tester in our testing lab.
For more information, please contact us at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
And for further reading, please find the referenced standards at:
ISO 4649:2017: https://www.iso.org/standard/70325.html
ASTM D5963-4(2019): https://www.astm.org/Standards/D5963.htm
Kim Bini


